As the world's 19th-largest country, Mongolia offers a landscape that is as dramatic as it is expansive. From the snowy peaks of the west to the arid expanse of the south, let's take a journey through the geography of this fascinating landlocked nation.
Size and Elevation
Mongolia is a country defined by high altitude and massive distances. The country sits at a relatively high average elevation of 1,580 meters (5,180 ft). Even the capital city, Ulaanbaatar, rests high up at 1,350 meters.
WEST TO EAST
NORTH TO SOUTH
HIGHEST POINT
LOWEST POINT
2,400 km
1,260 km
Khüiten Peak
(4,374 m)
Lake Huh
(560 m)
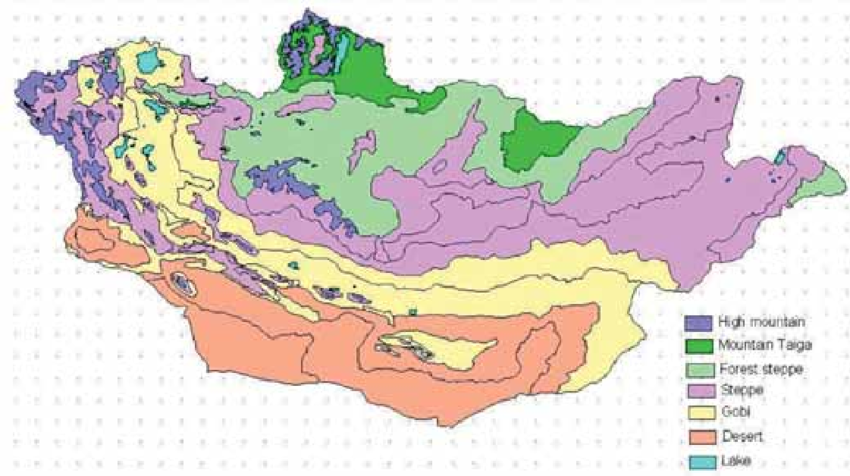
The Four Zones of Vegetation
Mongolia isn't just one endless grassy plain. The country's biology and landscape are divided into four distinct vegetation zones:
Mountain Forest
Steppe
Semi-desert
Desert
These zones create a diverse regional layout. If you travel to the North, you will find dense forests and mountain ranges. The West is famous for its high, snow-capped mountains and ancient glaciers.
Travel to the East, and you will encounter the classic Mongolian image: vast steppe plains and heaths. Finally, the South transforms into the arid Gobi Desert, desert steppe, and areas featuring low mountains.
Major Mountain Ranges

Three major mountain ranges dominate the Mongolian skyline, each with its own character:
The Altai Mountains: These are the highest and most rugged, stretching from the west to the southwest.
The Khangai Mountains: occupying much of central and northern Mongolia, these mountains are lush and iconic.
The Khentii Mountains: Located northeast of Ulaanbaatar near the Russian border, this range is lower in elevation than the others but historically significant.
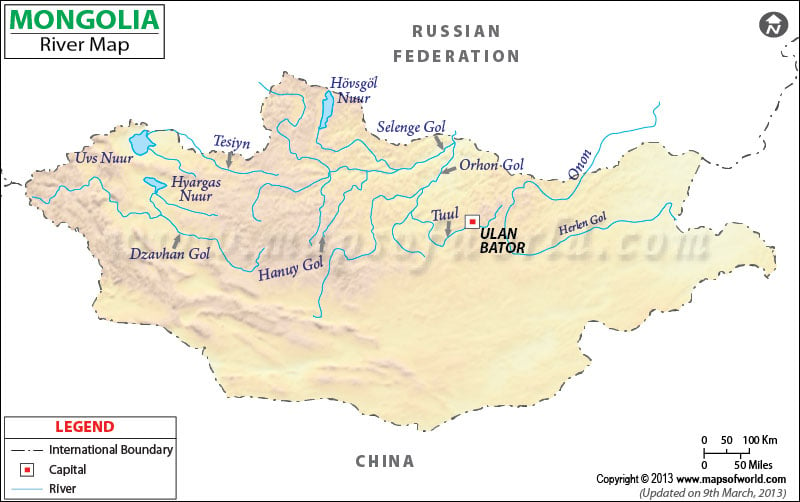
Lakes and Rivers
Despite being landlocked, Mongolia is rich in water sources, boasting numerous lakes and long, winding rivers.
Major Lakes
Lake Uvs: The largest lake by surface area, covering 3,350 square kilometers.
Lake Khovsgol: A massive freshwater lake covering 2,620 km².
Lake Khar Us: A significant body of water covering 1,852 km².
Major Rivers
The Orkhon: The longest river, flowing for 1,124 km.
The Kherlen: Stretching 1,090 km.
The Selenge: Flowing for 539 km.
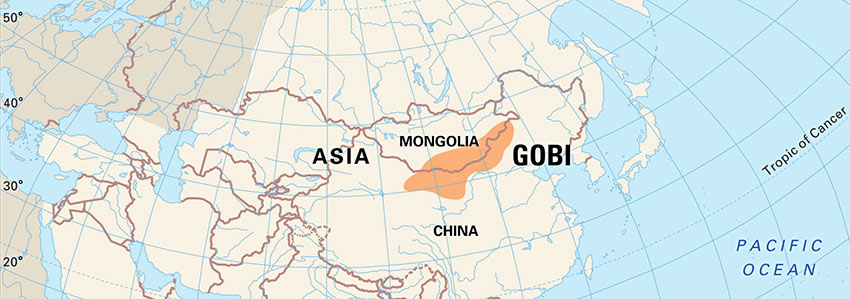
The Gobi Desert
No discussion of Mongolian geography is complete without mentioning the Gobi. Covering about one-third of Mongolia's surface, this isn't just a barren wasteland; it is a diverse ecosystem of desert and semi-desert terrain.
Historically, the Gobi was a crucial section of the Silk Road, serving as a bridge between East and West for trade, culture, and travel.